Describe the Process of Carbon Cycle
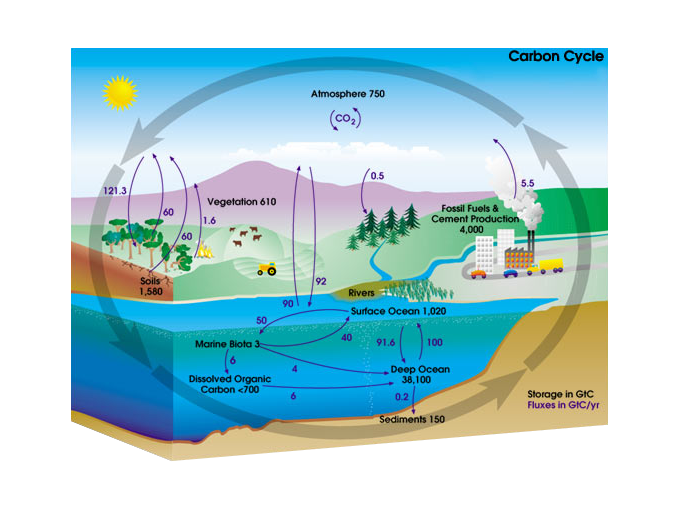
The source of the carbon found in living matter is carbon dioxide CO 2 in the air or dissolved in water. If all sources are equal to all sinks the carbon cycle can be said to be in equilibrium or in balance and there is no change in the size of the pools over time.
What Is The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis Decomposition Respiration And Combustion Earth How
Describe what makes a carbon sink and what makes a carbon source and give an example of each.

. Moving carbon throughout the ocean. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere or on Earth is constantly in flux. Carbon and oxygen are two elements that are essential to life.
2 carbon is transferred from the atmosphere to soil via carbon-fixing autotrophic organisms mainly photosynthesising plants and also photo- and chemoautotrophic microbes 3 4 that synthesise atmospheric carbon dioxide co 2 into organic material. These animals and plants eventually die and upon. Up to 24 cash back The Carbon Cycle Steps.
The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle. The Carbon Cycle Step 3. Name two ways that humans interfere with the natural carbon cycle.
Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe and is found in many forms on Earth. The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds many of which are essential to life on Earth.
Carbon can be stored in a variety of reservoirs including plants and animals which is why they are considered carbon life forms. The carbon cycle is the natural exchange of CO2 between the atmosphere and terrestrial and marine biomes. Plants soil and the ocean act as carbon sinks in.
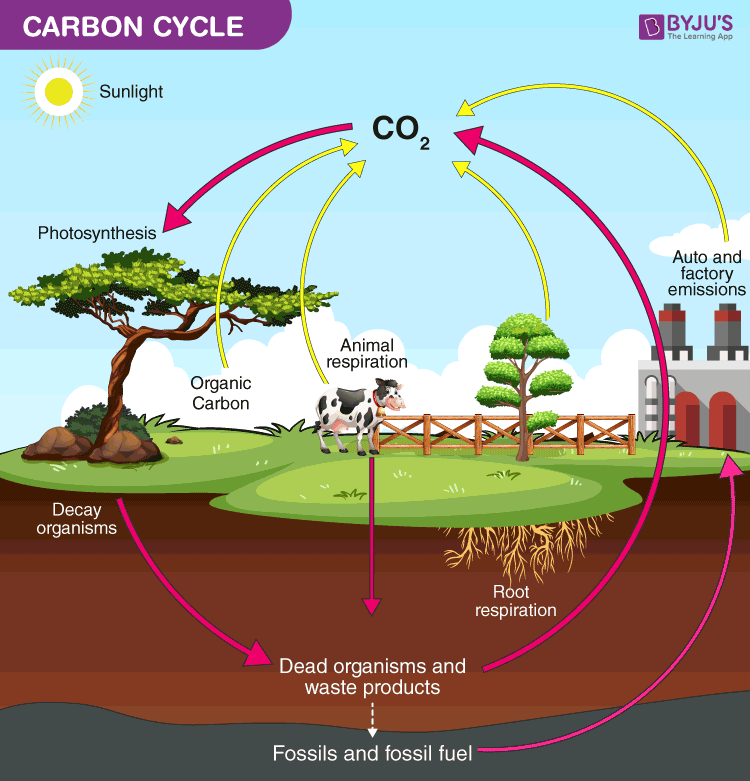
Respiration excretion and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil continuing the cycle. In this section we explore how these processes have led to changes in the dynamics of carbon in the atmosphere. Atmospheric oxygen comes mainly from green plants.
Animals that eat plants digest the sugar molecules to get energy for their bodies. Photosynthesis plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and form it into sugar starch and other organic. Processes in the forest carbon cycle game include photosynthesis respiration decomposition ingestion excretion combustion exudation and diffusion.
The phenomenon addressed in the proposed work has the opposite. Feeding moves carbon in the form of biological molecules along the food chain. They use energy from the sun to chemically combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen and oxygen from water to create sugar molecules.
The carbon and oxygen required for this process are obtained from CO2 and the energy for carbon fixation is derived from the ATP and NADPH produced during the photosynthesis process. Some soil processes promote carbon storage locking it away in stable forms resistant to decay. Because some carbon gases are greenhouse gases changes in the carbon cycle that put more carbon in the atmosphere also warm Earths climate.
Just like the terrestrial carbon cycle the oceanic biological carbon pump is all about photosynthesizing respiring eating producing waste products dying and decomposing. These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon gets bioaccumulated into their bodies. Processes of Carbon Flow in the Human Realm Humans have exerted an enormous influence on the global carbon cycle largely through deforestation and fossil fuel burning.
The biological pump plays a major role in. The Carbon Cycle Step 4. Following are the major steps involved in the process of the carbon cycle.
The forms range from carbon dioxide CO₂ gas which is also termed a greenhouse gas to solids such as diamonds or graphite. Because theyre always circulating between the soil the air and the water living matters constantly renewed. The work is important because soil carbon is a major reservoir in the global carbon cycle storing about three times the amount of carbon contained in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
The biological carbon cycle Carbon enters all food webs both terrestrial and aquatic through autotrophs or self-feeders. The basic idea is that plants capture light energy and use it to split water molecules and then combine the products with carbon dioxide to make carbohydrates which are used for fuel and construction of the plant. Name two ways that carbon is stored for a very long time in the natural cycle.
CO 2 H 2 Olight energyCH 2 OO 2. Almost all of these autotrophs are photosynthesizers such as plants or algae. Oxygen is a by-product of this reaction which is summarized as.
The Carbon Cycle Step 2. Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration breathing and combustion burning. The carbon cycle begins with the process of photosynthesis which transforms inorganic.
They are naturally present in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide and gaseous oxygen. On the one hand this process interferes with the productivity of calcite-skeleton. The carbon cycle Figure 1 is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the bio-.
Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis. Processes involved in the carbon cycle are. Your teacher will set up the stations and tickets for the Lodgepole Pine Forest carbon cycle game.
Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land ocean and life through biological chemical geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle. Carbon is passed from the atmosphere as carbon dioxide to living things passed from one organism to the next in complex molecules and returned to the atmosphere as. Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
The conversion of CO2 to carbohydrate is called Calvin Cycle or C3 cycle and is named after Melvin Calvin who discovered it. The Earths carbon reservoirs naturally act as both sources adding carbon to the atmosphere and sinks removing carbon from the atmosphere. Other ocean carbon cycle feedbacks relate to the phenomenon of ocean acidification which results from the fact that increasing atmospheric CO 2 leads to increased dissolved bicarbonate ion in the ocean a phenomenon will discuss further in our next lesson on climate change impacts.
Carbon cycle in biology circulation of carbon in various forms through nature. Interest in the carbon cycle. These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon gets bio accumulated into their bodies.
The terrestrial carbon cycle is dominated by the balance between photosynthesis and respiration. Autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Transforming carbon compounds into new forms of carbon compounds.
Following are the main steps that are involved in the process of the carbon cycle. Carbon is used by plants to build leaves and stems which are then digested by animals and used for cellular growth. Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment the amount of carbon in this system does not change.
The Carbon Cycle Step 1.
The Carbon Cycle Definition Significance Steps And Land Oceanic Cycle
Carbon Cycle Definition Process Diagram Of Carbon Cycle
The Carbon Cycle Definition Significance Steps And Land Oceanic Cycle
Comments
Post a Comment